10. Directory Services¶
FreeNAS® supports integration with these directory services:
- Active Directory (for Windows 2000 and higher networks)
- LDAP
- NIS
FreeNAS® also supports Kerberos Realms, Kerberos Keytabs, and the ability to add more parameters to Kerberos Settings.
This section summarizes each of these services and the available configuration options within the FreeNAS® web interface.
10.1. Active Directory¶
Active Directory (AD) is a service for sharing resources in a Windows network. AD can be configured on a Windows server that is running Windows Server 2000 or higher or on a Unix-like operating system that is running Samba version 4. Since AD provides authentication and authorization services for the users in a network, it is not necessary to recreate the same user accounts on the FreeNAS® system. Instead, configure the Active Directory service so account information and imported users can be authorized to access the SMB shares on the FreeNAS® system.
Many changes and improvements have been made to Active Directory support within FreeNAS®. It is strongly recommended to update the system to the latest FreeNAS® 11.2 before attempting Active Directory integration.
Ensure name resolution is properly configured before configuring the Active Directory service. ping the domain name of the Active Directory domain controller from Shell on the FreeNAS® system. If the ping fails, check the DNS server and default gateway settings in on the FreeNAS® system.
Add a DNS record for the FreeNAS® system on the Windows server and verify the hostname of the FreeNAS® system can be pinged from the domain controller.
Active Directory relies on Kerberos, a time-sensitive protocol. The time on both the FreeNAS® system and the Active Directory Domain Controller cannot be out of sync by more than a few minutes.
To ensure both systems are set to the same time:
- use the same NTP server (set in on the FreeNAS® system)
- set the same timezone
- set either localtime or universal time at the BIOS level
Using a FreeNAS® system as an AD server and connecting to it with a FreeNAS® client requires additional configuration. On the AD server, go to and create a new internal or intermediate Certificate Authority (CA). Click (Options) and View for the CA and copy the Certificate and Private Key.
On the client web interface, select . Set Encryption Mode to TLS and SASL wrapping to sign. Go to and click ADD. Create a unique Identifier, set Type to Import CA, and paste the AD server CA certificate and private keys in those fields. Click Save and continue configuring AD.
Figure 10.1.1 shows settings.
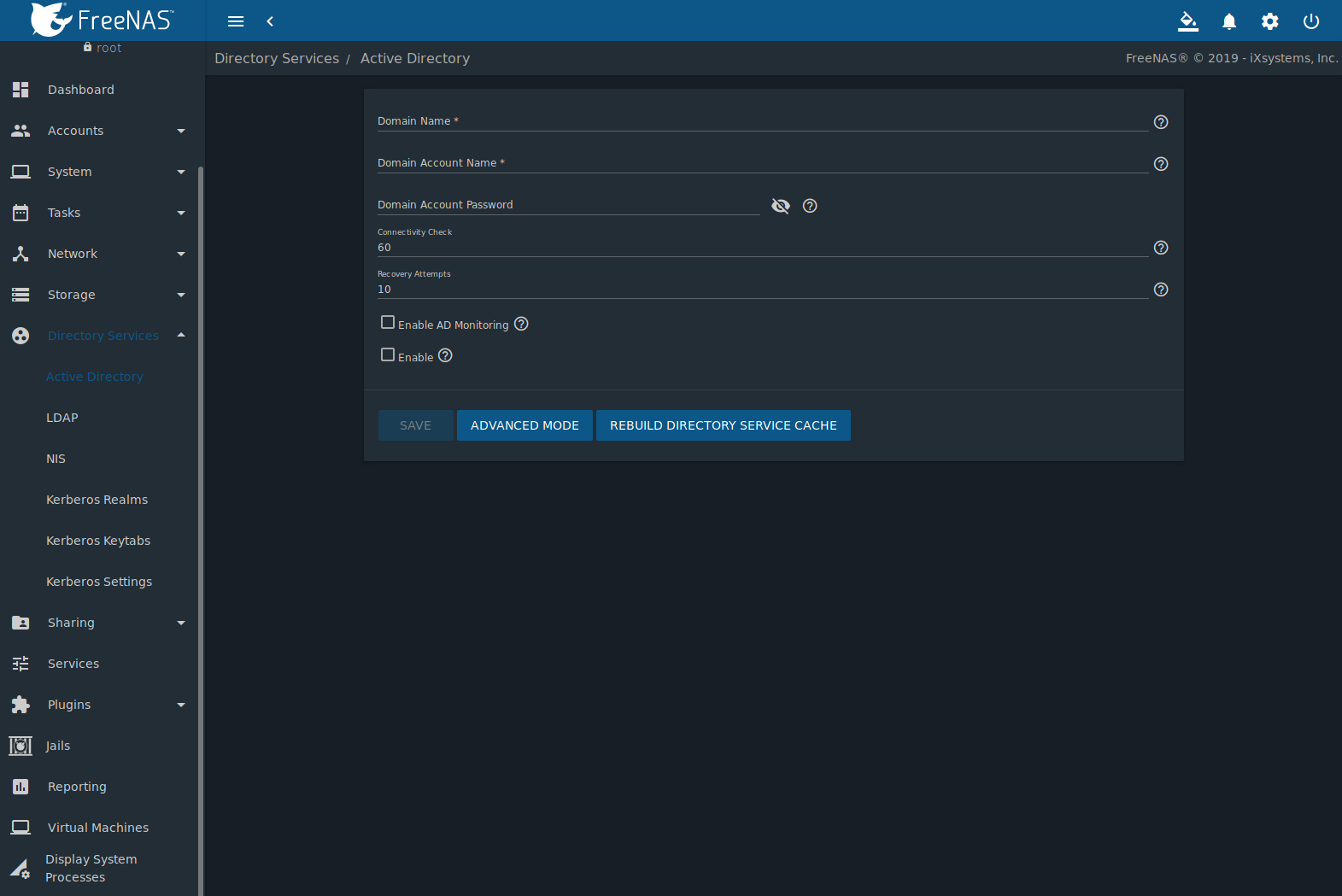
Fig. 10.1.1 Configuring Active Directory
Table 10.1.1 describes the configurable options. Some settings are only available in Advanced Mode. Click the ADVANCED MODE button to show the Advanced Mode settings. Go to and set the Show advanced fields by default option to always show advanced options.
| Setting | Value | Advanced Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain Name | string | Name of the Active Directory domain (example.com) or child domain (sales.example.com). This field is mandatory. Save will be inactive until valid input is entered. | |
| Domain Account Name | string | Name of the Active Directory administrator account. This field is mandatory. Save will be inactive until valid input is entered. | |
| Domain Account Password | string | Password for the Active Directory administrator account. Required the first time a domain is configured. Subsequent edits do not require the password. | |
| Connectivity Check | integer | How often for the system to verify Active Directory services are functioning. Enter a number of seconds. | |
| Recovery Attempts | integer | Number of times to attempt reconnecting to the Active Directory server. Tries forever when set to 0. | |
| Enable AD Monitoring | checkbox | Restart Active Directory automatically if the service disconnects. Setting this prevents configuring the Domain Controller service. | |
| Encryption Mode | drop-down | ✓ | Choices are Off, SSL (LDAPS protocol port 636), or TLS (LDAP protocol port 389). See http://info.ssl.com/article.aspx?id=10241 and https://hpbn.co/transport-layer-security-tls/ for more information about SSL and TLS. |
| Certificate | drop-down menu | ✓ | Select the Active Directory server certificate if SSL connections are used. If a certificate does not exist, create a Certificate Authority, then create a certificate on the Active Directory server. Import the certificate to the FreeNAS® system using the Certificates menu. To clear a saved certificate, choose the blank entry and click SAVE. |
| Verbose logging | checkbox | ✓ | Set to log attempts to join the domain to /var/log/messages. |
| UNIX extensions | checkbox | ✓ | Only set if the AD server is explicitly configured to map permissions for UNIX users. Setting provides persistent UIDs and GUIDs. Leave unset to map users and groups to the UID or GUID range configured in Samba. |
| Allow Trusted Domains | checkbox | ✓ | Only set when the network has active domain/forest trusts and managing file on multiple domains is required. Setting this option will generate more winbindd traffic and slow down filtering through user and group information. |
| Use Default Domain | checkbox | ✓ | Unset to prepend the domain name to the username. Unset to prevent name collisions when Allow Trusted Domains is set and multiple domains use the same username. |
| Allow DNS updates | checkbox | ✓ | Set to enable Samba to do DNS updates when joining a domain. |
| Disable FreeNAS Cache | checkbox | ✓ | Set to disable caching AD users and groups. This can help when unable to bind to a domain with a large number of users or groups. |
| Site Name | string | ✓ | The relative distinguished name of the site object in Active Directory. |
| Domain Controller | string | ✓ | The server that manages user authentication and security as part of a Windows domain. Leave empty for FreeNAS® to use the DNS SRV records to automatically detect and connect to the domain controller. If the domain controller must be set manually, enter the server hostname or IP address. |
| Global Catalog Server | string | ✓ | The global catalog server holds a full set of attributes for the domain in which it resides and a subset of attributes for all objects in the Microsoft Active Directory Forest. See the IBM Knowledge Center. Leave empty for FreeNAS® to use the DNS SRV records to automatically detect and connect to the server. If the global catalog server must be entered manually, enter the server hostname or IP address. |
| Kerberos Realm | drop-down menu | ✓ | Select the realm created using the instructions in Kerberos Realms. |
| Kerberos Principal | drop-down menu | ✓ | Browse to the location of the keytab created using the instructions in Kerberos Keytabs. |
| AD Timeout | integer | ✓ | Increase the number of seconds before timeout if the AD service does not immediately start after connecting to the domain. |
| DNS Timeout | integer | ✓ | Increase the number of seconds before a timeout occurs if AD DNS queries timeout. |
| Idmap backend | drop-down menu and Edit Idmap button | ✓ | Choose the backend to map Windows security identifiers (SIDs) to UNIX UIDs and GIDs. See Table 10.1.2 for a summary of the available backends. Click Edit Idmap to configure the selected backend. |
| Windbind NSS Info | drop-down menu | ✓ | Choose the schema to use when querying AD for user/group information. rfc2307 uses the RFC2307 schema support included in Windows 2003 R2, sfu is for Services For Unix 3.0 or 3.5, and sfu20 is for Services For Unix 2.0. |
| SASL wrapping | drop-down menu | ✓ | Choose how LDAP traffic is transmitted. Choices are plain (plain text), sign (signed only), or seal (signed and encrypted). Windows 2000 SP3 and newer can be configured to enforce signed LDAP connections. |
| Enable | checkbox | Set to enable the Active Directory service. | |
| Netbios Name | string | ✓ | Limited to 15 characters. Automatically populated with the original hostname of the system. This must be different from the Workgroup name. |
| NetBIOS alias | string | ✓ | Limited to 15 characters. |
Table 10.1.2 summarizes the backends which are available in the Idmap backend drop-down menu. Each backend has its own man page that gives implementation details. Since selecting the wrong backend will break Active Directory integration, a pop-up menu will appear whenever changes are made to this setting.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| ad | AD server uses RFC2307 or Services For Unix schema extensions. Mappings must be provided in advance by adding the uidNumber attributes for users and gidNumber attributes for groups in the AD. |
| autorid | Similar to rid, but automatically configures the range to be used for each domain, so there is no need to specify a specific range for each domain in the forest. The only needed configuration is the range of UID or GIDs to use for user and group mappings and an optional size for the ranges. |
| fruit | Generate IDs as macOS does. The UID and GID can be identical on all FreeNAS® servers on the network. For use in LDAP environments where Apple’s Open Directory is the authoritative LDAP server. |
| ldap | Stores and retrieves mapping tables in an LDAP directory service. Default for LDAP directory service. |
| nss | Provides a simple means of ensuring that the SID for a Unix user is reported as the one assigned to the corresponding domain user. |
| rfc2307 | An AD server is required to provide the mapping between the name and SID and an LDAP server is required to provide the mapping between the name and the UID/GID. |
| rid | Default for AD. Requires an explicit idmap configuration for each domain, using disjoint ranges where a writeable default idmap range is to be defined, using a backend like tdb or ldap. |
| script | Stores mapping tables for clustered environments in the winbind_cache tdb. |
| tdb | Default backend used by winbindd for storing mapping tables. |
| tdb2 | Substitute for tdb used by winbindd in clustered environments. |
Click the REBUILD DIRECTORY SERVICE CACHE button if a new Active Directory user needs immediate access to FreeNAS®. This occurs automatically once a day as a cron job.
If there are problems connecting to the realm, verify
the settings do not include any disallowed characters. Active Directory
does not allow $ characters in Domain or NetBIOS names. The
length of those names is also limited to 15 characters. The
Administrator account password cannot contain the $ character. If a
$ exists in the domain administrator password,
kinit reports a “Password Incorrect” error and
ldap_bind reports an “Invalid credentials (49)” error.
It can take a few minutes after configuring the Active Directory service for the AD information to be populated to the FreeNAS® system. Once populated, the AD users and groups will be available in the drop-down menus of the Permissions screen of a dataset.
The Active Directory users and groups that are imported to the FreeNAS® system are shown by typing commands in the FreeNAS® Shell:
- View users: wbinfo -u
- View groups: wbinfo -g
In addition, wbinfo -t tests the connection and, if successful, shows a message similar to:
checking the trust secret for domain YOURDOMAIN via RPC calls succeeded
To manually check that a specified user can authenticate, enter
net ads join -S dcname -U username.
getent passwd and getent group can provide more troubleshooting information if no users or groups are listed in the output.
Tip
Sometimes network users do not appear in the drop-down menu of a Permissions screen but the wbinfo commands display these users. This is typically due to the FreeNAS® system taking longer than the default ten seconds to join Active Directory. Increase the value of AD timeout to 60 seconds.
To change a certificate, enable Advanced Mode, set the Encryption Mode to Off, then disable AD by unchecking Enable. Click SAVE. Select the new Certificate, set the Encryption Mode as desired, check Enable to re-enable AD, and click SAVE to restart AD.
10.1.1. Troubleshooting Tips¶
When running AD in a 2003/2008 mixed domain, this forum post has instructions to prevent the secure channel key from becoming corrupt.
Active Directory uses DNS to determine the location of the domain
controllers and global catalog servers in the network. Use
host -t srv _ldap._tcp.domainname.com to determine the SRV
records of the network and change the weight and/or priority of the SRV
record to reflect the fastest server. More information about SRV records
can be found in the Technet article
How DNS Support for Active Directory Works.
The realm used depends on the priority in the SRV DNS record. DNS can override the system Active Directory settings. When unable to connect to the correct realm, check the SRV records on the DNS server.
An expired password for the administrator account will cause kinit to fail. Ensure the password is still valid and double-check the password on the AD account being used does not include any spaces, special symbols, and is not unusually long.
If the Windows server version is lower than 2008 R2, try creating a Computer entry on the Windows server Organizational Unit (OU). When creating this entry, enter the FreeNAS® hostname in the name field. Make sure it is under 15 characters, the same name as the one set in the Hostname field in , and the same NetBIOS alias in settings. Make sure the hostname of the domain controller is set in the Domain Controller field of .
10.1.2. If the System Does not Join the Domain¶
If the system will not join the Active Directory domain, run these commands in the order listed. echo commands will return a value of 0 and klist will show a Kerberos ticket:
If the cache becomes out of sync due to an AD server being taken off and back online, resync the cache using .
Note
If any of the commands fail or result in a traceback, create a bug report at https://bug.ixsystems.com that includes the commands in the order in which they were run and the exact wording of the error message or traceback.
sqlite3 /data/freenas-v1.db "update directoryservice_activedirectory set ad_enable=1;"
echo $?
service ix-kerberos start
service ix-nsswitch start
service ix-kinit start
service ix-kinit status
echo $?
klist
Next, only run these two commands if the UNIX extensions box is checked in Advanced Mode and a keytab has been uploaded using Kerberos Keytabs:
service ix-sssd start
service sssd start
Finally, run these commands. echo returns a 0 unless something has gone wrong:
python /usr/local/www/freenasUI/middleware/notifier.py start cifs
service ix-activedirectory start
service ix-activedirectory status
echo $?
python /usr/local/www/freenasUI/middleware/notifier.py restart cifs
service ix-pam start
service ix-cache start &
10.2. LDAP¶
FreeNAS® includes an OpenLDAP client for accessing information from an LDAP server. An LDAP server provides directory services for finding network resources such as users and their associated permissions. Examples of LDAP servers include Microsoft Server (2000 and newer), Mac OS X Server, Novell eDirectory, and OpenLDAP running on a BSD or Linux system. If an LDAP server is running on the network, configure the FreeNAS® LDAP service so network users can authenticate to the LDAP server and have authorized access to the data stored on the FreeNAS® system.
Note
LDAP authentication for SMB shares is disabled unless the LDAP directory has been configured for and populated with Samba attributes. The most popular script for performing this task is smbldap-tools. The LDAP server must support SSL/TLS and the certificate for the LDAP server CA must be imported with . Non-CA certificates are not currently supported.
Tip
Apple’s Open Directory is an LDAP-compatible directory service into which FreeNAS® can be integrated. The forum post FreeNAS with Open Directory in Mac OS X environments has more information.
Figure 10.2.1 shows the LDAP Configuration section from .
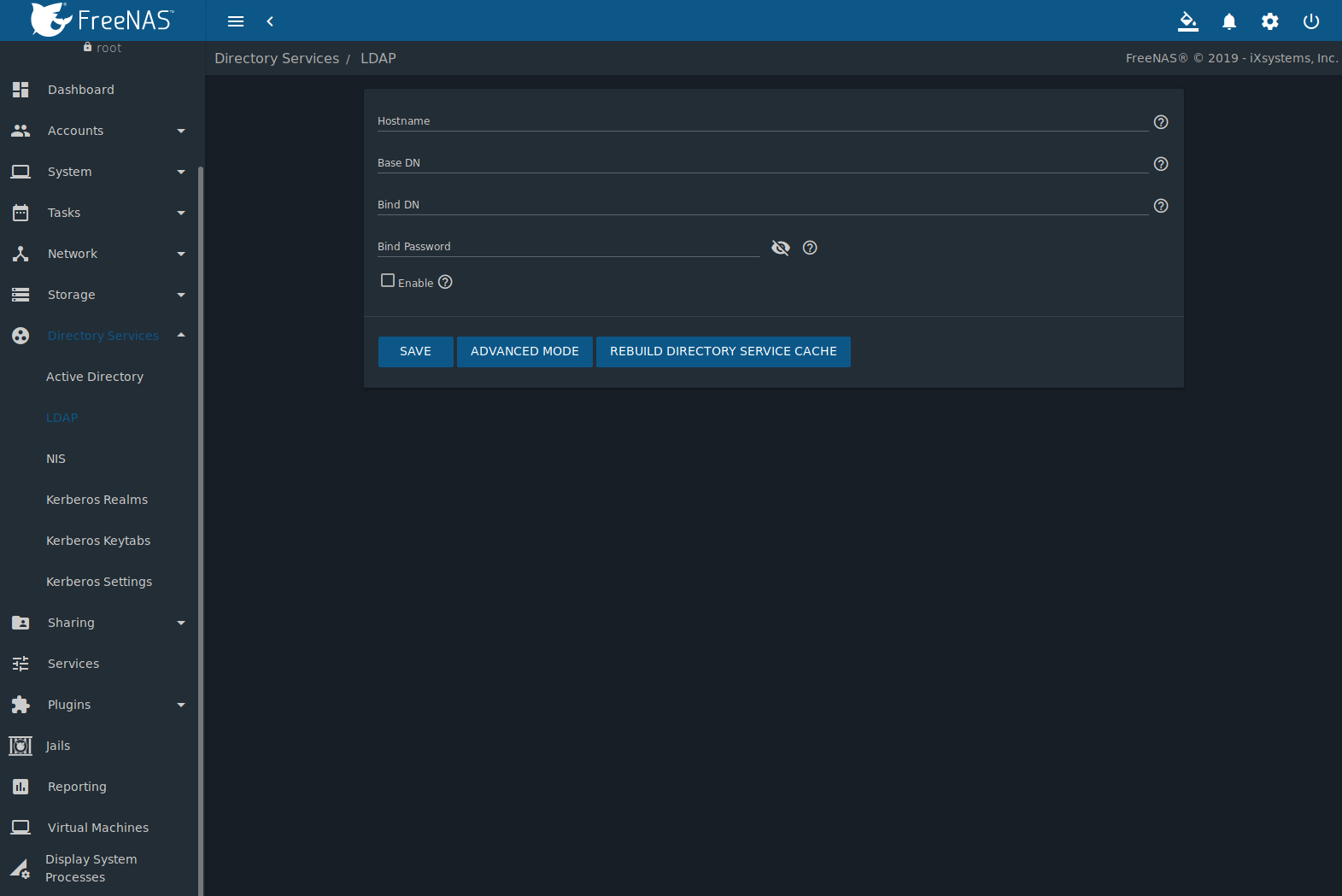
Fig. 10.2.1 Configuring LDAP
Table 10.2.1 summarizes the available configuration options. Some settings are only available in Advanced Mode. Click the ADVANCED MODE button to show the Advanced Mode settings. Go to and set the Show advanced fields by default option to always show advanced options.
Those new to LDAP terminology should read the OpenLDAP Software 2.4 Administrator’s Guide.
| Setting | Value | Advanced Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hostname | string | Hostname or IP address of the LDAP server. | |
| Base DN | string | Top level of the LDAP directory tree to be used when searching for resources (Example: dc=test,dc=org). | |
| Bind DN | string | Administrative account name on the LDAP server (Example: cn=Manager,dc=test,dc=org). | |
| Bind Password | string | Password for the Bind DN. Click SHOW/HIDE PASSWORDS to view or obscure the password characters. | |
| Allow Anonymous Binding | checkbox | ✓ | Instruct the LDAP server to disable authentication and allow read and write access to any client. |
| User Suffix | string | ✓ | Optional suffix to add to a name when the user account is added to the LDAP directory (Example: dept. company name). |
| Group Suffix | string | ✓ | Optional suffix to add to a name when the group is added to the LDAP directory (Example: dept. or company name). |
| Password Suffix | string | ✓ | Optional suffix to add to the password when the password is added to the LDAP directory. |
| Machine Suffix | string | ✓ | Optional suffix to add to the name when the system is added to the LDAP directory (Example: server, accounting). |
| SUDO Suffix | string | ✓ | The suffix for LDAP-based users that need superuser access. |
| Kerberos Realm | drop-down menu | ✓ | The realm created using the instructions in Kerberos Realms. |
| Kerberos Principal | drop-down menu | ✓ | The location of the principal in the keytab created as described in Kerberos Keytabs. |
| Encryption Mode | drop-down menu | ✓ | Choices are Off, SSL, or TLS. Note: SSL or TLS and a Certificate must be selected for authentication to work. SSL selects LDAPS protocol (port 636). TLS selects LDAP protocol (port 389). |
| Certificate | drop-down menu | ✓ | The LDAP CA certificate. The certificate for the LDAP server CA must first be imported using the menu. A certificate is required to use authentication |
| LDAP timeout | integer | ✓ | Increase this value in seconds if obtaining a Kerberos ticket times out. |
| DNS timeout | integer | ✓ | Increase this value in seconds if DNS queries timeout. |
| Idmap Backend | drop-down menu | ✓ | The backend used to map Windows security identifiers (SIDs) to UNIX UIDs and GIDs. See Table 10.1.2 for a summary of the available backends. Click EDIT IDMAP to configure the selected backend. |
| Samba Schema | checkbox | ✓ | Set if LDAP authentication for SMB shares is required and the LDAP server is already configured with Samba attributes. |
| Auxiliary Parameters | string | ✓ | Additional options for sssd.conf(5). |
| Schema | drop-down menu | ✓ | If Samba Schema is set, select the schema to use. Choices are rfc2307 and rfc2307bis. |
| Enable | checkbox | Unset to disable the configuration without deleting it. | |
| Netbios Name | string | ✓ | Limited to 15 characters. Automatically populated with the original hostname of the system. This must be different from the Workgroup name. |
| NetBIOS alias | string | ✓ | Limited to 15 characters. |
Note
FreeNAS® automatically appends the root DN. This means the scope and root DN are not to be included when configuring the user, group, password, and machine suffixes.
LDAP users and groups appear in the drop-down menus of the Permissions screen of a dataset after configuring the LDAP service. Type getent passwd in the FreeNAS® Shell to verify the users have been imported. Type getent group to verify the groups have been imported.
If the users and groups are not listed, refer to
Common errors encountered when using OpenLDAP Software
for common errors and how to fix them. When troubleshooting LDAP, open
the FreeNAS® Shell and look for error messages in
/var/log/auth.log.
To clear LDAP users and groups from FreeNAS®, go to , clear the Hostname field, unset Enable, and click SAVE. Confirm LDAP users and groups are cleared by going to the and viewing the output of the getent passwd and getent group commands.
10.3. NIS¶
The Network Information Service (NIS) maintains and distributes a central directory of Unix user and group information, hostnames, email aliases, and other text-based tables of information. If an NIS server is running on the network, the FreeNAS® system can be configured to import the users and groups from the NIS directory.
Click the Rebuild Directory Service Cache button if a new NIS user needs immediate access to FreeNAS®. This occurs automatically once a day as a cron job.
Note
In Windows Server 2016, Microsoft removed the Identity Management for Unix (IDMU) and NIS Server Role. See Clarification regarding the status of Identity Management for Unix (IDMU) & NIS Server Role in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview and beyond.
Figure 10.3.1 shows the section. Table 10.3.1 summarizes the configuration options.
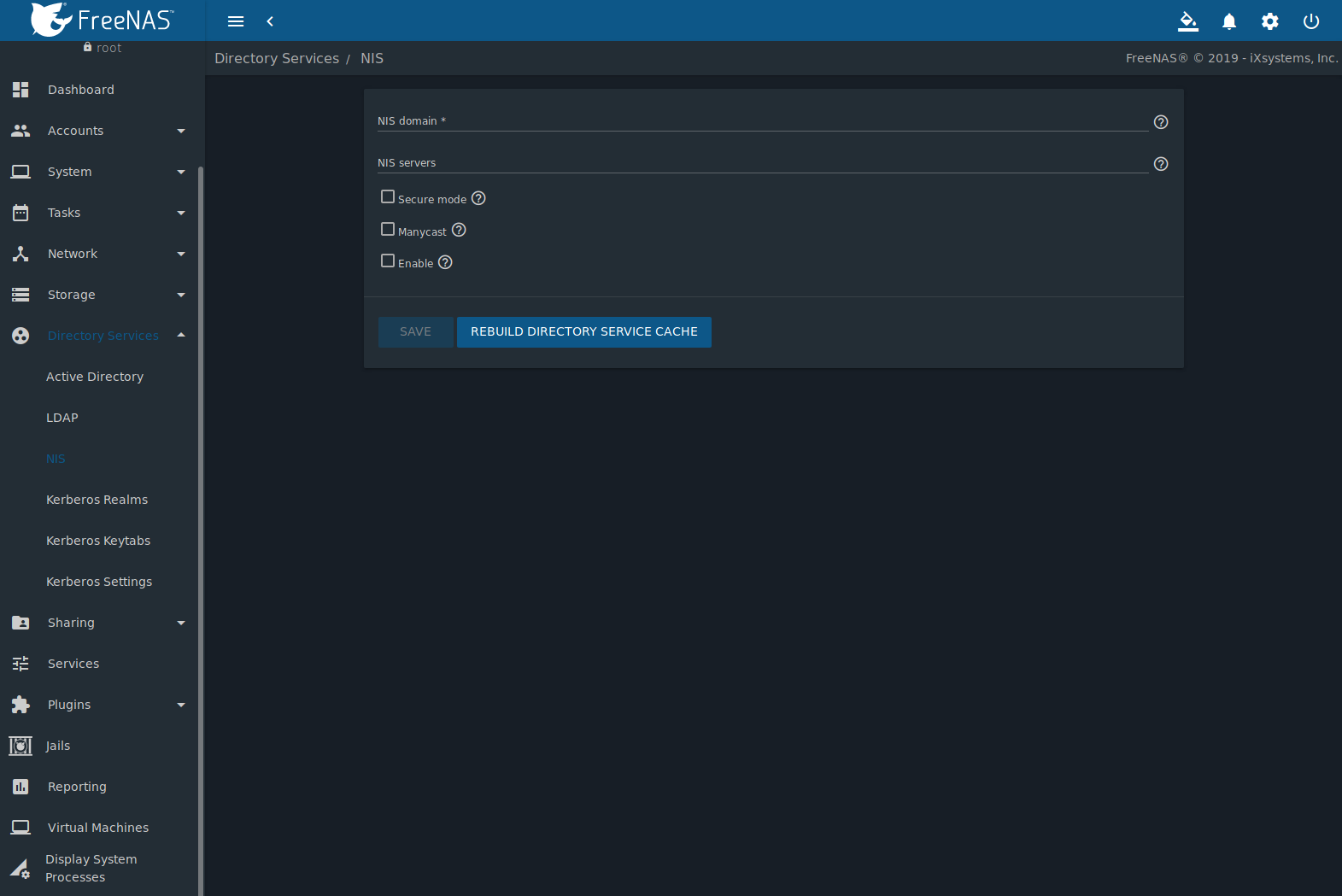
Fig. 10.3.1 NIS Configuration
| Setting | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NIS domain | string | Name of NIS domain. |
| NIS servers | string | Comma-delimited list of hostnames or IP addresses. |
| Secure mode | checkbox | Set to have ypbind(8) refuse to bind to any NIS server not running as root on a TCP port over 1024. |
| Manycast | checkbox | Set to have ypbind to bind to the server that responds the fastest. This is useful when no local NIS server is available on the same subnet. |
| Enable | checkbox | Unset to disable the configuration without deleting it. |
10.4. Kerberos Realms¶
A default Kerberos realm is created for the local system in FreeNAS®. can be used to view and add Kerberos realms. If the network contains a Key Distribution Center (KDC), click ADD to add the realm. The configuration screen is shown in Figure 10.4.1.
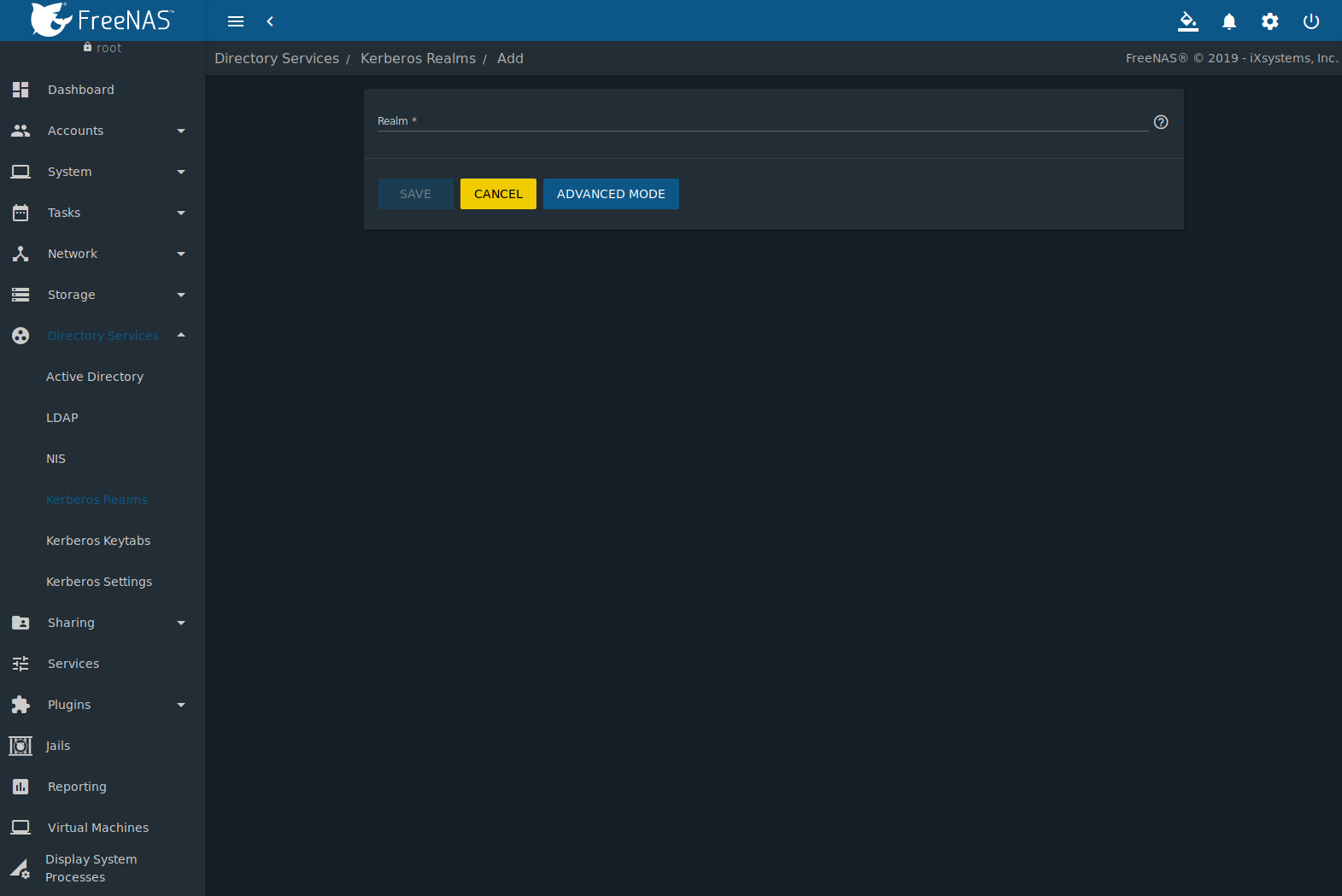
Fig. 10.4.1 Adding a Kerberos Realm
Table 10.4.1 summarizes the configurable options. Some settings are only available in Advanced Mode. To see these settings, either click ADVANCED MODE or configure the system to always display these settings by setting Show advanced fields by default in .
| Setting | Value | Advanced Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Realm | string | Name of the realm. | |
| KDC | string | ✓ | Name of the Key Distribution Center. |
| Admin Server | string | ✓ | Server where all changes to the database are performed. |
| Password Server | string | ✓ | Server where all password changes are performed. |
10.5. Kerberos Keytabs¶
Kerberos keytabs are used to do Active Directory or LDAP joins without a password. This means the password for the Active Directory or LDAP administrator account does not need to be saved into the FreeNAS® configuration database, which is a security risk in some environments.
When using a keytab, it is recommended to create and use a less privileged account for performing the required queries as the password for that account will be stored in the FreeNAS® configuration database. To create the keytab on a Windows system, use the ktpass command:
ktpass.exe /out freenas.keytab /princ http/useraccount@EXAMPLE.COM /mapuser useraccount /ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL /crypto ALL /pass userpass
where:
freenas.keytabis the file to upload to the FreeNAS® server.useraccountis the name of the user account for the FreeNAS® server generated in Active Directory Users and Computers.http/useraccount@EXAMPLE.COMis the principal name written in the format host/user.account@KERBEROS.REALM. By convention, the kerberos realm is written in all caps, but make sure the case used for the Kerberos Realm matches the realm name. See this note about using/princfor more details.userpassis the password associated withuseraccount.
Setting /crypto to ALL allows using all supported
cryptographic types. These keys can be specified instead of ALL:
- DES-CBC-CRC is used for compatibility.
- DES-CBC-MD5 adheres more closely to the MIT implementation and is used for compatibility.
- RC4-HMAC-NT uses 128-bit encryption.
- AES256-SHA1 uses AES256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96 encryption.
- AES128-SHA1 uses AES128-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96 encryption.
This will create a keytab with sufficient privileges to grant tickets.
After the keytab is generated, add it to the FreeNAS® system using .
To instruct the Active Directory service to use the keytab, select the installed keytab using the drop-down Kerberos Principal menu in Advanced Mode. When using a keytab with Active Directory, make sure that username and userpass in the keytab matches the Domain Account Name and Domain Account Password fields in .
To instruct LDAP to use a principal from the keytab, select the principal from the drop-down Kerberos Principal menu in Advanced Mode.
10.6. Kerberos Settings¶
Configure additional Kerberos parameters in the section. Figure 10.6.1 shows the fields available:
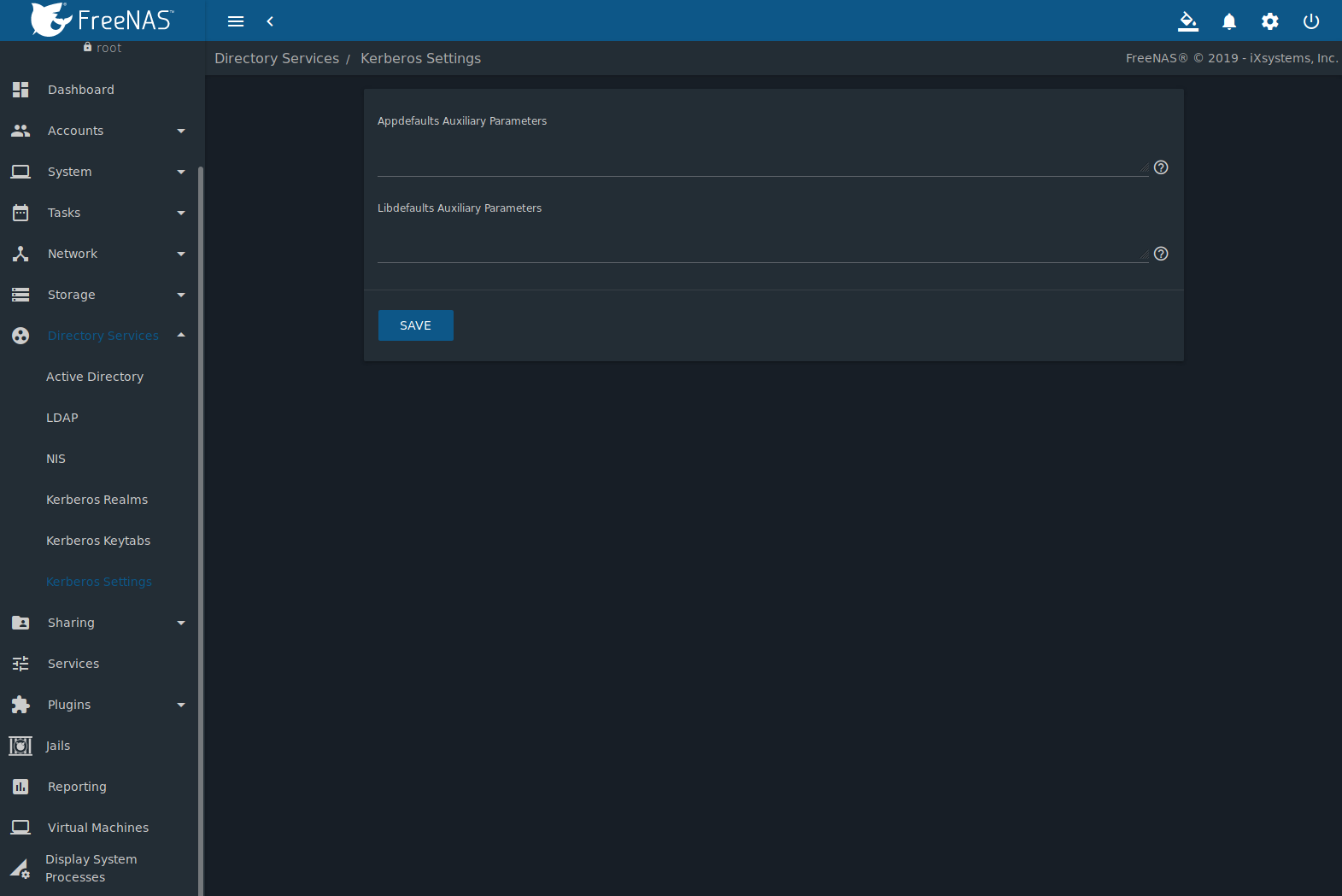
Fig. 10.6.1 Additional Kerberos Settings
- Appdefaults Auxiliary Parameters: Define any additional settings for use by some Kerberos applications. The available settings and syntax is listed in the [appdefaults] section of krb.conf(5).
- Libdefaults Auxiliary Parameters: Define any settings used by the Kerberos library. The available settings and their syntax are listed in the [libdefaults] section of krb.conf(5).