16. Reporting¶
Reporting displays several graphs, as seen in Figure 16.1. Choose a category from the drop-down menu to view those graphs. There are also options to change the graph view and number of graphs on each page.
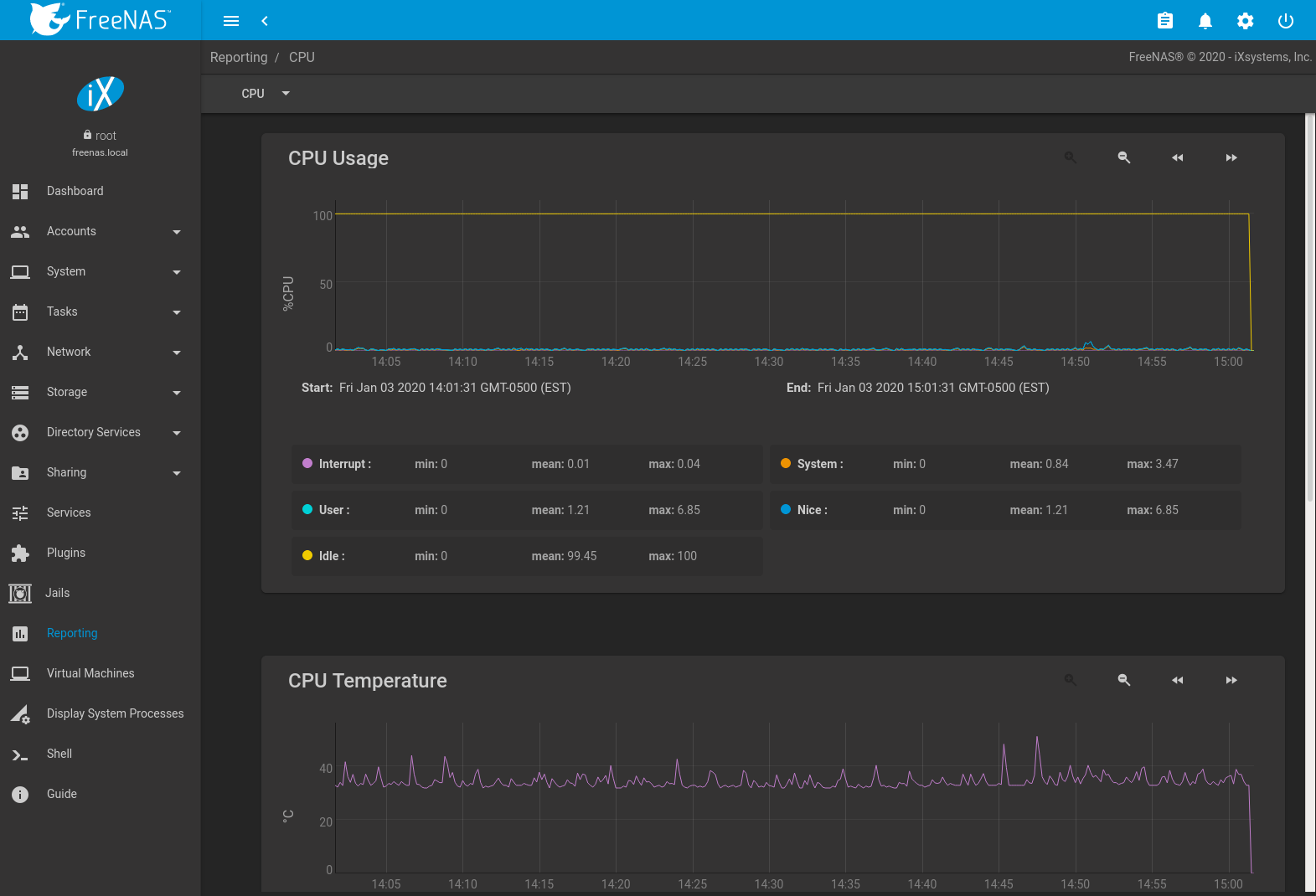
Fig. 16.1 Reporting Graphs
FreeNAS® uses collectd to provide reporting statistics. For a clearer picture, hover over a point in the graph to show exact numbers for that point in time. Use the magnifier buttons next to each graph to increase or decrease the displayed time increment from 10 minutes, hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly. The << and >> buttons scroll through the output.
Note
Reporting graphs do not appear if there is no related data.
Graphs are grouped by category on the Reporting page:
CPU
- CPU shows the amount of time spent by the CPU in various states such as executing user code, executing system code, and being idle. Graphs of short-, mid-, and long-term load are shown, along with CPU temperature graphs.
Disk
- Disk shows read and write statistics on I/O, percent busy, latency, operations per second, pending I/O requests, and disk temperature. Choose the DEVICES and METRICS to view the selected metrics for the chosen devices.
Note
Temperature monitoring for the disk is disabled if HDD Standby is enabled in Disks.
Memory
Network
- Interface shows received and transmitted traffic in megabytes per second for each configured interface.
NFS
- NFS shows information about the number of procedure calls for each procedure and whether the system is a server or client.
Partition
- Disk space displays free, used, and reserved space for each pool and dataset. However, the disk space used by an individual zvol is not displayed as it is a block device.
System
- Processes displays the number of processes. It is grouped by state.
Target
- Target shows bandwidth statistics for iSCSI ports.
UPS
- UPS displays statistics about an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) using Network UPS tools. Statistics include voltages, currents, power, frequencies, load, and temperatures.
ZFS
- ZFS shows compressed physical ARC size, hit ratio, demand data, demand metadata, and prefetch data.
Reporting data is saved to permit viewing and monitoring usage trends over time. This data is preserved across system upgrades and restarts.
Data files are saved in /var/db/collectd/rrd/.
Warning
Reporting data is frequently written and should not be stored on the boot pool or operating system device.